We know students in the middle grades can make an argument to throw a pizza party, to get out of detention or to prove a point. So, why do they find it hard to craft strong arguments from text? The skill of argumentative or persuasive writing is a skill that’s easier said than done.
Close reading naturally lends itself to teaching argumentative writing. To be sure, it’s not the only way to culminate a close-reading lesson, but as students read, reread and break down text, analyzing author’s arguments and crafting their own can come naturally.
Argumentative writing isn’t persuasion, and it’s not about conflict or winning. Instead, it’s about creating a claim and supporting that claim with evidence. For example, in this set of writing samples from Achieve the Core, fifth grade students read an article about homework and wrote an argument in response to the question How much homework is too much? One student wrote the claim: I think that students should have enough homework but still have time for fun. Students in third grade should start having 15 minutes a night and work up to a little over an hour by sixth grade. The student goes on to support her claim with evidence from the article she read. It builds responsibility and gives kids a chance to practice.

Here are four ways to build your students’ ability to write arguments through close reading.
Choose Text Wisely
I don’t think I can say it enough: The most important part of planning close reading is choosing the text. If you want students to be able to create and support an argument, the text has to contain evidence—and lots of it. Look for texts or passages that are worth reading deeply (read: well written with intriguing, worthwhile ideas) and that raise interesting questions that don’t have a right or wrong answer.
PEELS: Help Students Structure Their Arguments
Before students can get creative with their writing, make sure they can structure their arguments. In the PEELS approach, students need to:
- Make a point.
- Support it with evidence (and examples).
- Explain their evidence.
- Link their points.
- Maintain a formal style.
Check out this Teachers Pay Teachers resource (free) for an explanation and graphic organizer to use with students.
Provide Time for Collaboration
When students are allowed to talk about their writing, they craft stronger arguments because they’re provided time to narrow and sharpen their ideas. In his book, Translating Talk Into Text (2014) Thomas McCann outlines two types of conversation that help students prepare to write.
- Exploratory discussions: These small-group discussions provide space for students to find out what others are thinking and explore the range of possibilities. These conversations should happen after students have read closely, with the goal of building an understanding of what ideas or claims are present within a text.
- Drafting discussions: After students have participated in exploratory discussion, drafting discussions are a chance for students to come together as a whole group to share and refine their ideas. Drafting discussions start by sharing arguments that students discussed in the exploratory discussions, then provide time for students to explore the arguments and challenge one another. The goal is for students to end the discussion with a clear focus for their writing.
The Incredible Shrinking Argument: Help Students Synthesize
Once students are writing, probably the biggest challenge becomes whittling an argument down to the essentials. To help students do this, have them write their argument on a large sticky note (or in a large text box). Then, have them whittle it twice by revising it and rewriting it on smaller sticky notes (or text boxes) to get the excess ideas or details out. By the time they’re rewriting it on the smallest sticky note (or textbox), they’ll be forced to identify the bones of their argument. (See The Middle School Mouth blog for more on this strategy.)
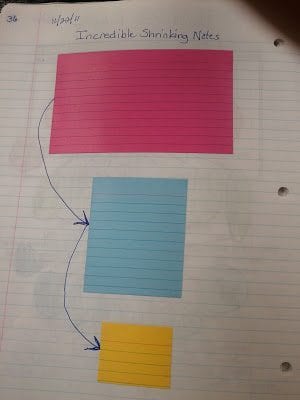
(Photo from The Middle School Mouth)
Samantha Cleaver is an education writer, former special education teacher and avid reader. Her book, Every Reader a Close Reader, is scheduled to be published by Rowman and Littlefield in 2015. Read more at her blog www.cleaveronreading.wordpress.com.

